Redis的事件循环机制
众所周知,Redis服务器是单线程架构,且能够同时并发地服务多个客户端。其实现方式是怎样的呢?背后主要包含两大机制:IO多路复用(IO Multiplexing)机制,以及事件循环(Eventloop)机制。本篇主要介绍事件循环机制,当然不可避免的会涉及到IO多路复用机制(例如:Linux下的epoll)。
事件(Event)
讲解事件循环之前,我们先了解一下什么是事件?有哪些事件?事件的作用是什么?等基础概念。
事件是Redis服务器处理内部任务的最小单位,包括时间事件(Time Event)和文件事件(File Event)两类。典型的时间事件是周期性打印连接的客户端的统计信息,典型的文件事件是某一个客户端的get命令请求。正是通过事件,Redis服务器才能够完成各种周期性的、用户触发的任务,进而维持自身的稳定运行以及满足客户端的请求。
时间事件(Time Event)
时间事件记录着那些要在指定时间点运行的事件,多个时间事件以无序链表的形式保存在服务器状态中。结构体如下:
/* Time event structure */
typedef struct aeTimeEvent {
long long id; /* time event identifier. */
long when_sec; /* seconds */
long when_ms; /* milliseconds */
aeTimeProc *timeProc;
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc;
void *clientData;
struct aeTimeEvent *next;
} aeTimeEvent;
时间事件又可以分为一次性执行事件和多次执行事件,主要根据上述结构体中的函数timeProc所执行的结果来判断,如果返回为AE_NOMORE,表示单次执行事件,执行完毕之后就会被从时间事件链表中删除掉。相反,如果返回一个整型数值,则表示等待相应时长的毫秒数之后被再次执行。核心处理函数如下:
/* Process time events */
static int processTimeEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
int processed = 0;
aeTimeEvent *te;
long long maxId;
te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
maxId = eventLoop->timeEventNextId-1;
while(te) {
long now_sec, now_ms;
long long id;
if (te->id > maxId) {
te = te->next;
continue;
}
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
if (now_sec > te->when_sec ||
(now_sec == te->when_sec && now_ms >= te->when_ms))
{
int retval;
id = te->id;
retval = te->timeProc(eventLoop, id, te->clientData);
processed++;
/* After an event is processed our time event list may
* no longer be the same, so we restart from head.
* Still we make sure to don't process events registered
* by event handlers itself in order to don't loop forever.
* To do so we saved the max ID we want to handle.
*
* FUTURE OPTIMIZATIONS:
* Note that this is NOT great algorithmically. Redis uses
* a single time event so it's not a problem but the right
* way to do this is to add the new elements on head, and
* to flag deleted elements in a special way for later
* deletion (putting references to the nodes to delete into
* another linked list). */
if (retval != AE_NOMORE) {
aeAddMillisecondsToNow(retval,&te->when_sec,&te->when_ms);
} else {
aeDeleteTimeEvent(eventLoop, id);
}
te = eventLoop->timeEventHead;
} else {
te = te->next;
}
}
return processed;
}
文件事件(File Event)
Redis服务器通过在多个客户端之间进行多路复用,从而实现高效的命令请求处理:多个客户端通过套接字连接到Redis服务器中,但只有在套接字可读或可写时,服务器才会和这些客户端进行交互。Redis将这类因为对套接字进行多路复用而产生的事件称为文件事件,文件事件可以分为读事件和写事件两类。结构体如下:
/* File event structure */
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;
读事件
读事件标志着客户端命令请求的发送状态。当一个新的客户端连接到服务器时,服务器会给为该客户端绑定读事件,直到客户端断开连接之后,这个读事件才会被移除。读事件在整个网络连接的生命期内,都会在等待和就绪两种状态之间切换:
- 当客户端只是连接到服务器,但并没有向服务器发送命令时,该客户端的读事件就处于等待状态。
- 当客户端给服务器发送命令请求,并且请求已到达时(相应的套接字可以执行读操作),该客户端的读事件处于就绪状态。
写事件
写事件标志着客户端对命令结果的接收状态。和客户端自始至终都关联着读事件不同,服务器只会在有命令结果要传回给客户端时,才会为客户端关联写事件,并且在命令结果传送完毕之后,客户端和写事件的关联就会被移除。一个写事件会在两种状态之间切换:
- 当服务器有命令结果需要返回给客户端,但客户端还不可写时,那么写事件处于等待状态。
- 当服务器有命令结果需要返回给客户端,并且客户端可写时,那么写事件处于就绪状态。
对于文件事件,不同的事件,需要关联不同的处理函数,放到事件循环部分介绍。
事件循环(Eventloop)
事件循环是对上述事件的循环处理,另外还包括一个在进入每一轮循环之前的一个预处理函数,如下图所示:
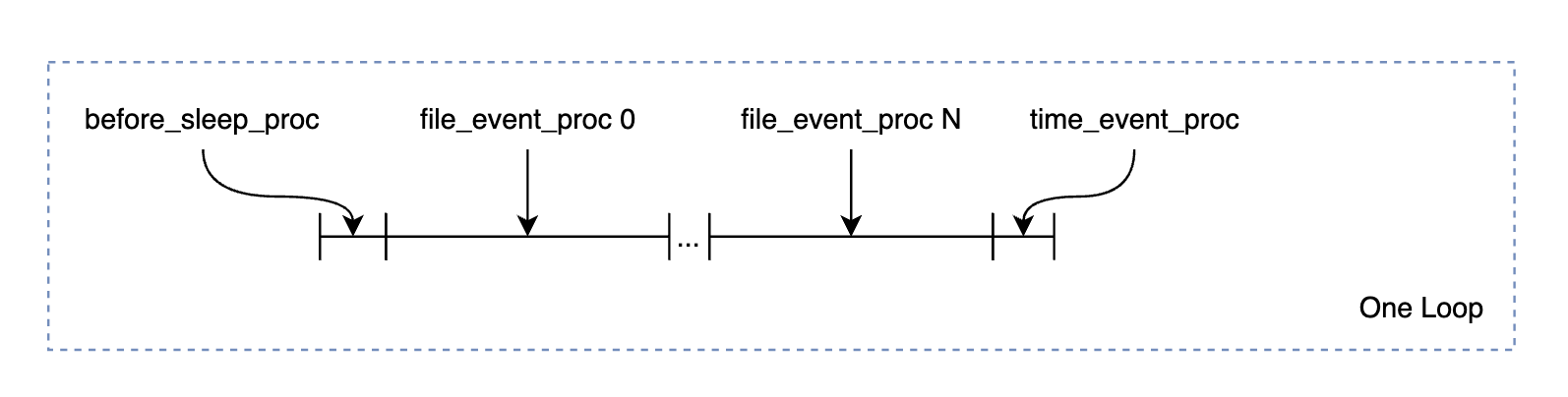
说明:这里会有0个或者N个文件事件得到处理
预处理函数会进行诸如将AOF文件的buffer写入磁盘等操作。
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS);
}
}
/* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event
* (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed).
* Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event
* fires, or when the next time event occurrs (if any).
*
* If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns.
* if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed.
* if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed.
* if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed.
* if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all
* the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed.
*
* The function returns the number of events processed. */
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
/* Note that we want call select() even if there are no
* file events to process as long as we want to process time
* events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready
* to fire. */
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop);
if (shortest) {
long now_sec, now_ms;
/* Calculate the time missing for the nearest
* timer to fire. */
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
tvp = &tv;
tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec;
if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) {
tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000;
tvp->tv_sec --;
} else {
tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000;
}
if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0;
if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0;
} else {
/* If we have to check for events but need to return
* ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to se the timeout
* to zero */
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* Otherwise we can block */
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */
}
}
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
上述处理函数中值得注意的是numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);,这里tvp表示距离最近即将需要执行的时间事件的时间间隔。在aeApiPoll函数内部,作为等待就绪的文件事件的最大等待时长,也就是说,在最近的一个时间事件发生之前,如果没有文件事件处于就绪状态,那么在等待超时之后,直接执行最近的时间事件;反之,如果有文件事件需要处理,那么就会立马先执行文件事件,再处理事件事件,如果执行文件事件的时间过长,那么约定的时间事件得到处理的时间就会被推迟。aeApiPoll函数如下:
static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
int retval, numevents = 0;
retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,AE_SETSIZE,
tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + tvp->tv_usec/1000) : -1);
if (retval > 0) {
int j;
numevents = retval;
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
int mask = 0;
struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j;
if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE;
if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd;
eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask;
}
}
return numevents;
}