Robotics for Programmers
This book isn’t complete.
Ch1: Robotics or Bits Meet Atoms
1.1 Robots and Other Machines
Characteristics:
- interact with physical world directly
- can be programmed to execute different tasks
1.2 What You Will Learn About Robots
1.3 Robotics: The Big Picture
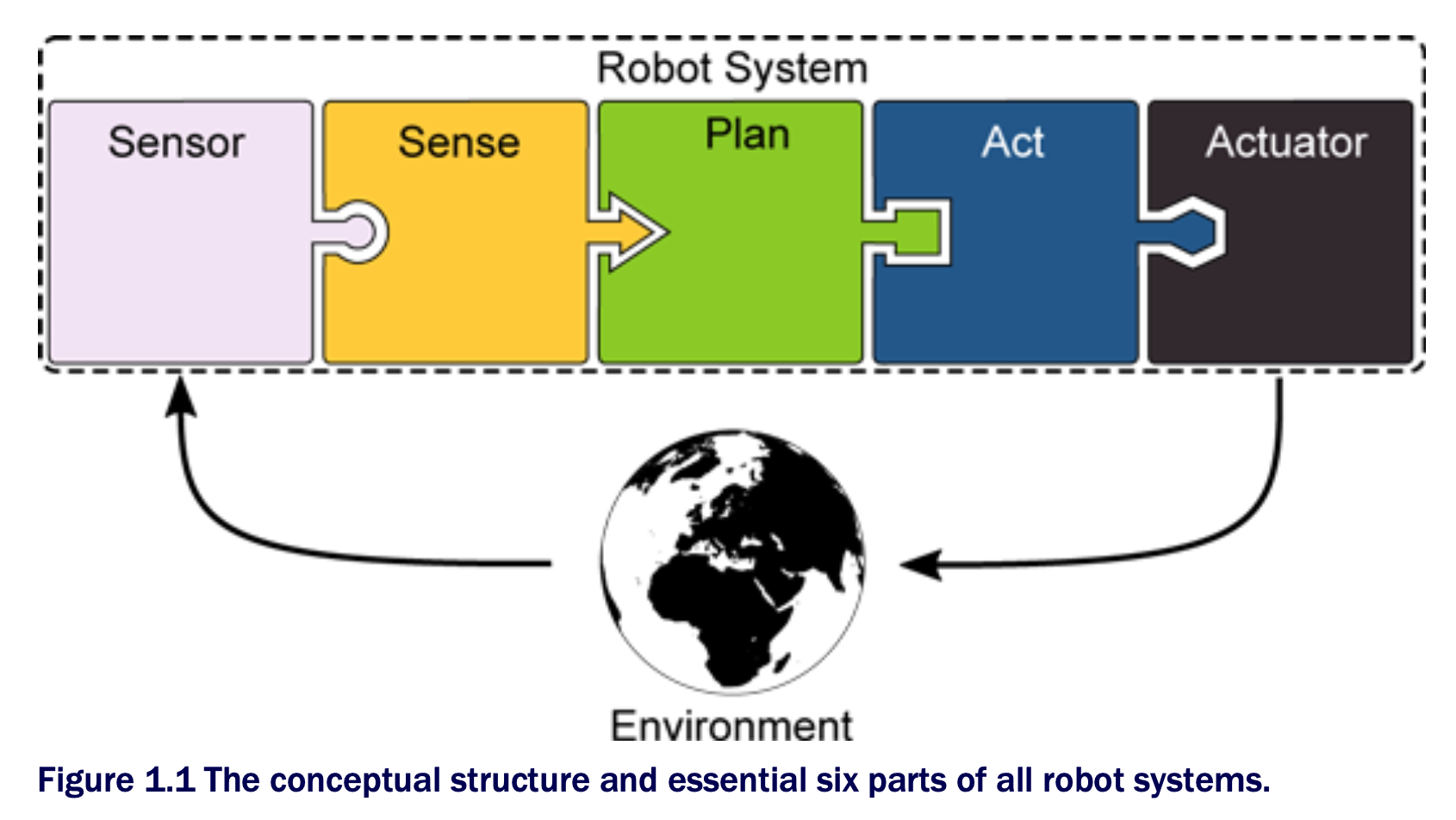
We could do more or less sensor data processing in the sensing part and leave more or less to the planning part. Author’s advice is: Everything related to getting information out of sensor data without considering the robot’s objectives is part of sensing.
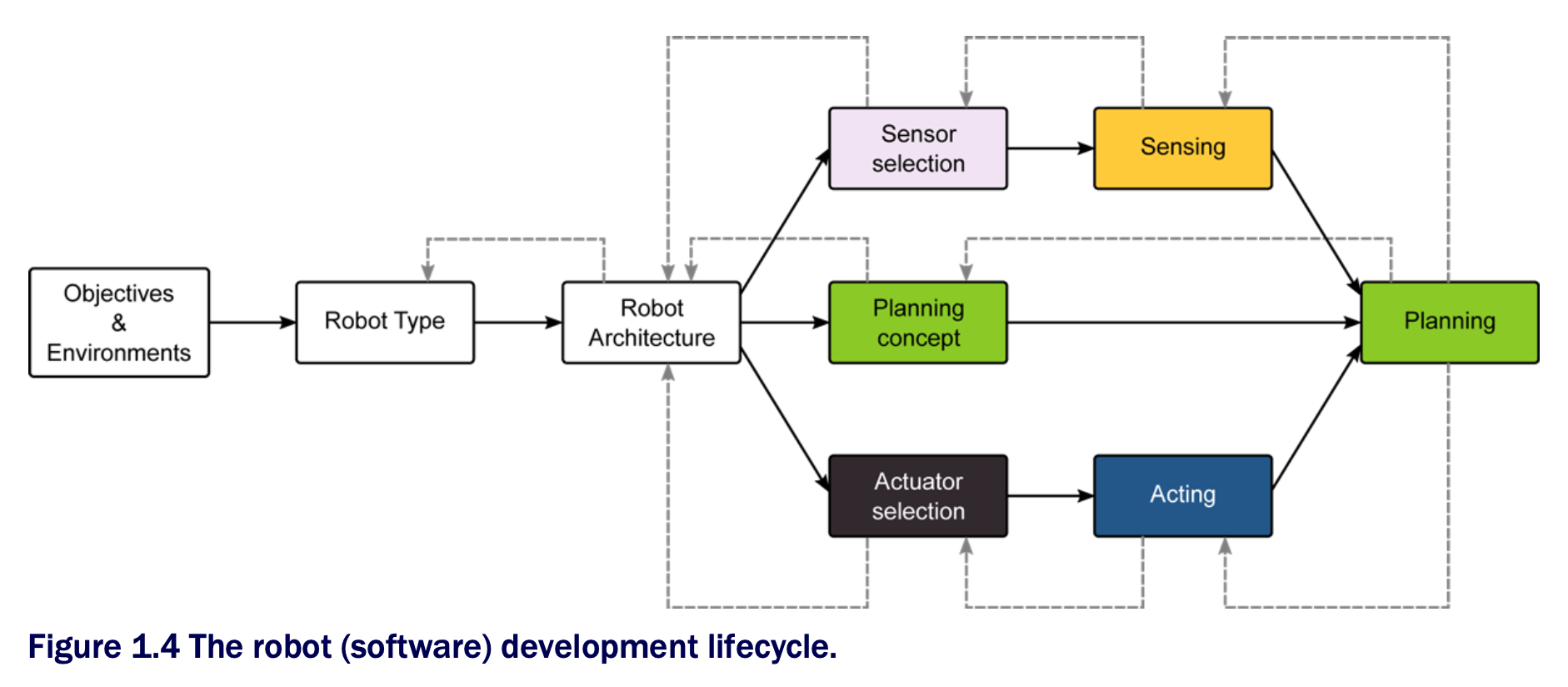
1.4 Robot Software Development Lifecycle
Ch2: Robots from a Software Point of View
2.1 Interacting with The Real World
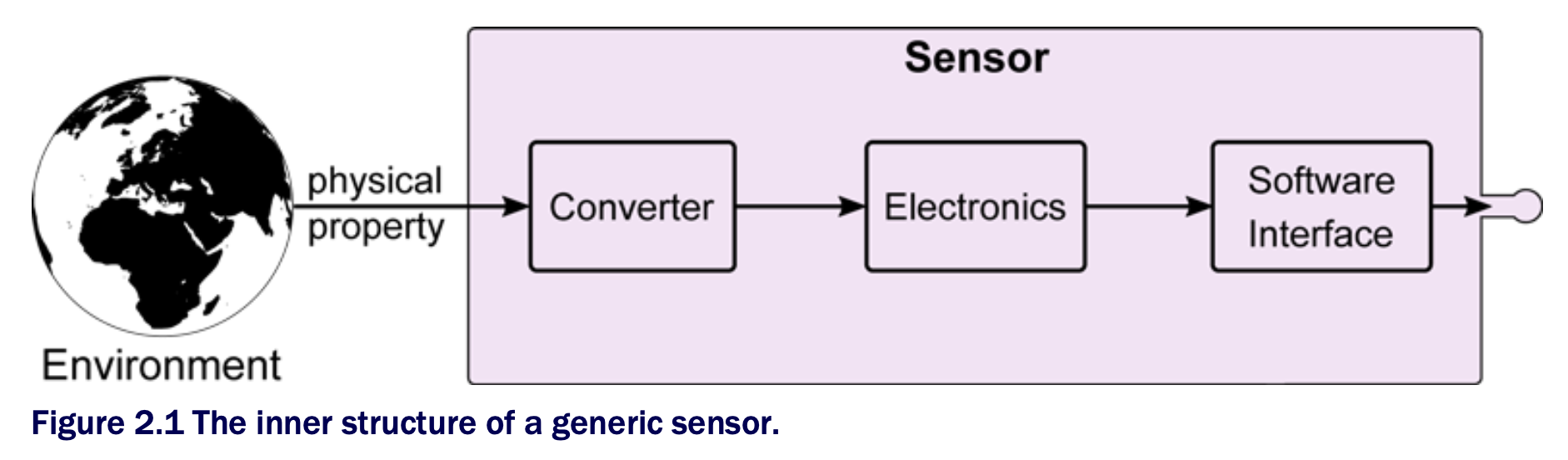
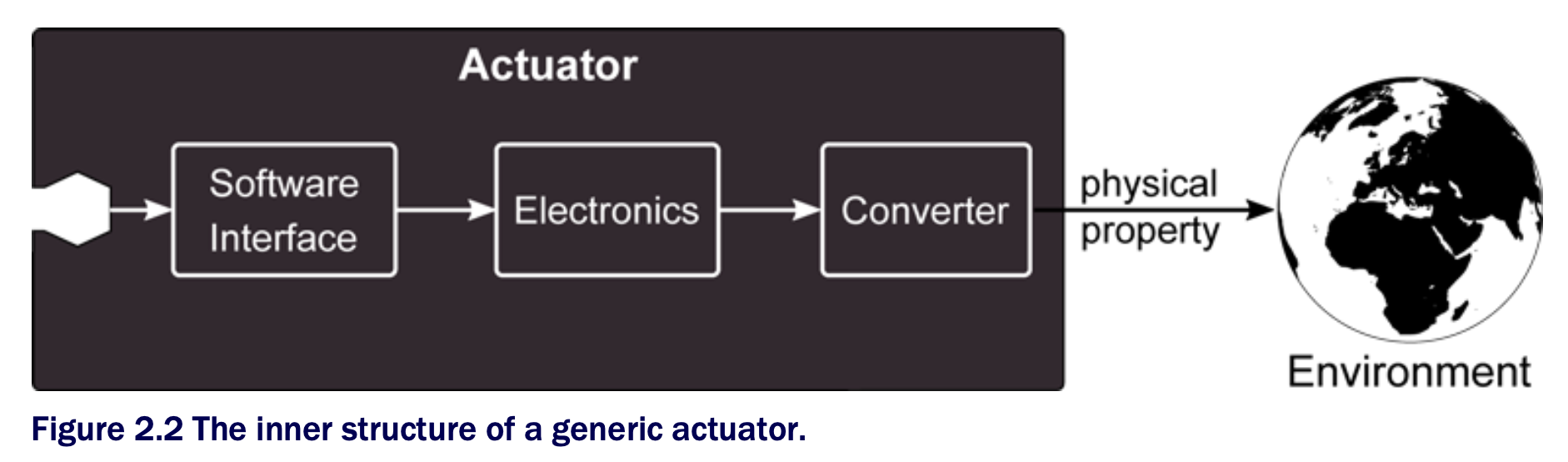
The generic inner structure of a sensor is shown in figure 2.1. The actuator’s inner structure is depicted in figure 2.2.
2.2 Types of Robots
Manipulators
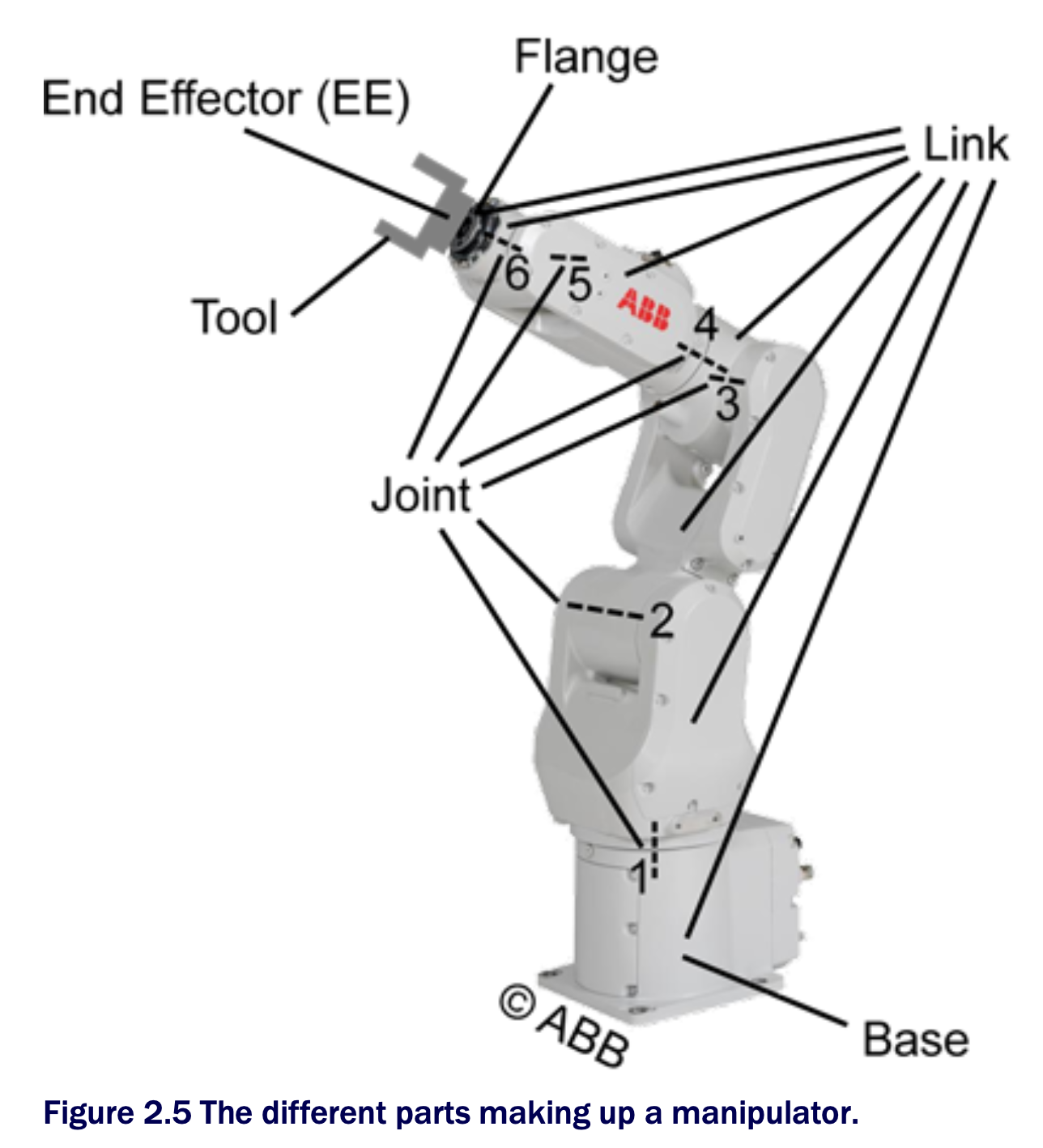
- Joint: the moveable parts in the robot hardware
- Link: a rigid mechanical part connecting the joints
- Base: the first link of the robot
- End Effector(EE): the last link of the robot
- Flange: a standardized mounting plate that allows to fasten tools to the last link of the robot
- Tool: a device attached to the flange that enables the robot to perform the intended process
To a large extent, robots are motion generating machines.
Abstract API for manipulators:
robot.move(pose)
Mobile Robots
Abstract API for mobile robots:
robot.navigate(pose)
Mobile Manipulators
There are two basic approaches for integrating the mobile and manipulation functionality:
- Independent successive
- Coupled simultaneous
2.3 Robot Sensor Basics
Position Sensors
we distinguish different types according to three criteria:
- Angular/Rotary versus Linear
- Absolute versus Incremental
- Single-turn vs Multi-turn (for rotary encoders only)
Abstract API for position sensor(encoder):
encoder.position()
Cameras
Apart from the resolution, another important property of cameras is their frame rate.
Abstract API for cameras:
camera.image()
2.4 Robot Sensing Basics
2.5 Robot Actuator Basics
Three most widely used types of electric motors in robotics:
- stepper motors
- (brushed) DC motors
- brushless DC motors